ravescape.ru
Learn
How Much Would It Cost To Get Solar Panels

Solar Panel Cost in California · On average, a solar system costs $12,$18, for a kW solar system in California · California homeowners can reduce the. A 4kW PV system could cost under $6, including professional design and all components. You still get the manufacturers warranty and keep all the tax credits. Solar panels for a home will cost between $25, and $50, before incentives are utilized. After utilizing the 30% federal tax credit, homeowners can expect. In , a typical residential solar system may set you back between $11, to $14, to install after tax credits and rebates. Solar energy is a long-term. On average, solar panels cost $ per square foot of living space, after factoring in the 30% tax credit. However, the cost per square foot varies based on. System Size and Estimated Solar Panel Costs. National averages for solar pricing at $ per square foot before accounting for the federal tax credit. After. Solar power systems are very custom based on the home, roof type, shading, and utility. Installation of panels for the average 5kW system ranges from. Installing solar panels costs an average of $27,, though it ranges between $3, and $55, based on system size, panel type, wattage, and more. Getting solar panels installed can vary quite a bit in cost depending on where you live and the size of your house. For my place, a mid-sized. Solar Panel Cost in California · On average, a solar system costs $12,$18, for a kW solar system in California · California homeowners can reduce the. A 4kW PV system could cost under $6, including professional design and all components. You still get the manufacturers warranty and keep all the tax credits. Solar panels for a home will cost between $25, and $50, before incentives are utilized. After utilizing the 30% federal tax credit, homeowners can expect. In , a typical residential solar system may set you back between $11, to $14, to install after tax credits and rebates. Solar energy is a long-term. On average, solar panels cost $ per square foot of living space, after factoring in the 30% tax credit. However, the cost per square foot varies based on. System Size and Estimated Solar Panel Costs. National averages for solar pricing at $ per square foot before accounting for the federal tax credit. After. Solar power systems are very custom based on the home, roof type, shading, and utility. Installation of panels for the average 5kW system ranges from. Installing solar panels costs an average of $27,, though it ranges between $3, and $55, based on system size, panel type, wattage, and more. Getting solar panels installed can vary quite a bit in cost depending on where you live and the size of your house. For my place, a mid-sized.
If you're going DIY and buying panels yourself, you're looking at around $ per panel ( watts x 1 dollar). Keep in mind that this is before tax rebates! The upfront price for an average-sized residential solar system has fallen from $40, in to about $25, today. Meanwhile, utility-scale solar now costs. It costs about $30, to install solar panels. That's a big number, but incentives usually lower it significantly. The average 6-kW residential solar panel installation is $ before incentives. Learn about cost factors, financing options, tax breaks and more. On average, solar panels cost $ per square foot of living space, after factoring in the 30% tax credit. However, the cost per square foot varies based on. According to a January article published by Forbes, the average cost of solar panels is $16,, which can double based on the average cost to install. Each solar panel can cost from $1, to $2,, depending on the quality of the panel and the company selling it. Batteries are another investment, one that. On average, businesses can anticipate an initial investment ranging from $, to $,+ for their solar system, taking into account the system size and. The average installed cost ($/watt) for a residential solar electric system has dropped significantly since the s and is between $$/watt. That. So, How Much Would Solar Panels Cost for a 1, Square Foot House? Solar panels for a 1, square foot house cost roughly $18,, with average pricing in the. A typical residential PV array is perhaps between 5 kW and 8 kW. So at $ the contract price would be $k ~ $28k Or net after tax rebate. The cost of a solar system installation can vary widely when you compare the efficiency rate of the solar panels and other installation expenses. The best solar. The average cost for solar equipment in the US, based on our analysis, is around $ per watt. To put this in perspective, this means that after the 30%. Each solar panel can cost from $1, to $2,, depending on the quality of the panel and the company selling it. Batteries are another investment, one that. Looking at national average pricing data, we found that the cost of owning a 5 kW solar system ranges from $13, to $21,, or from $ to $ per watt. It would be about $25K before the 30% tax credit. That is for about a 10 kW system on a barrel tile roof, which roughly matches my $ monthly power bill in. Installing a solar panel system costs an average of $27,, and that price has been falling over time. Most homeowners pay between $18, and $36, Expect. Polycrystalline silicon solar panels costs vary from $2 to $3 per watt. Thin-film solar panels are constructed from thin layers of various materials such as. Hardware costs include the actual equipment that make up a solar panel system: panels, solar inverters, mounting hardware, wiring and potentially, home. In New York, the average cost of a solar panel system ranges from around $30, to $50, before tax credits. The cost-per-watt in New York averages around.
Basics Of Stocks And Bonds
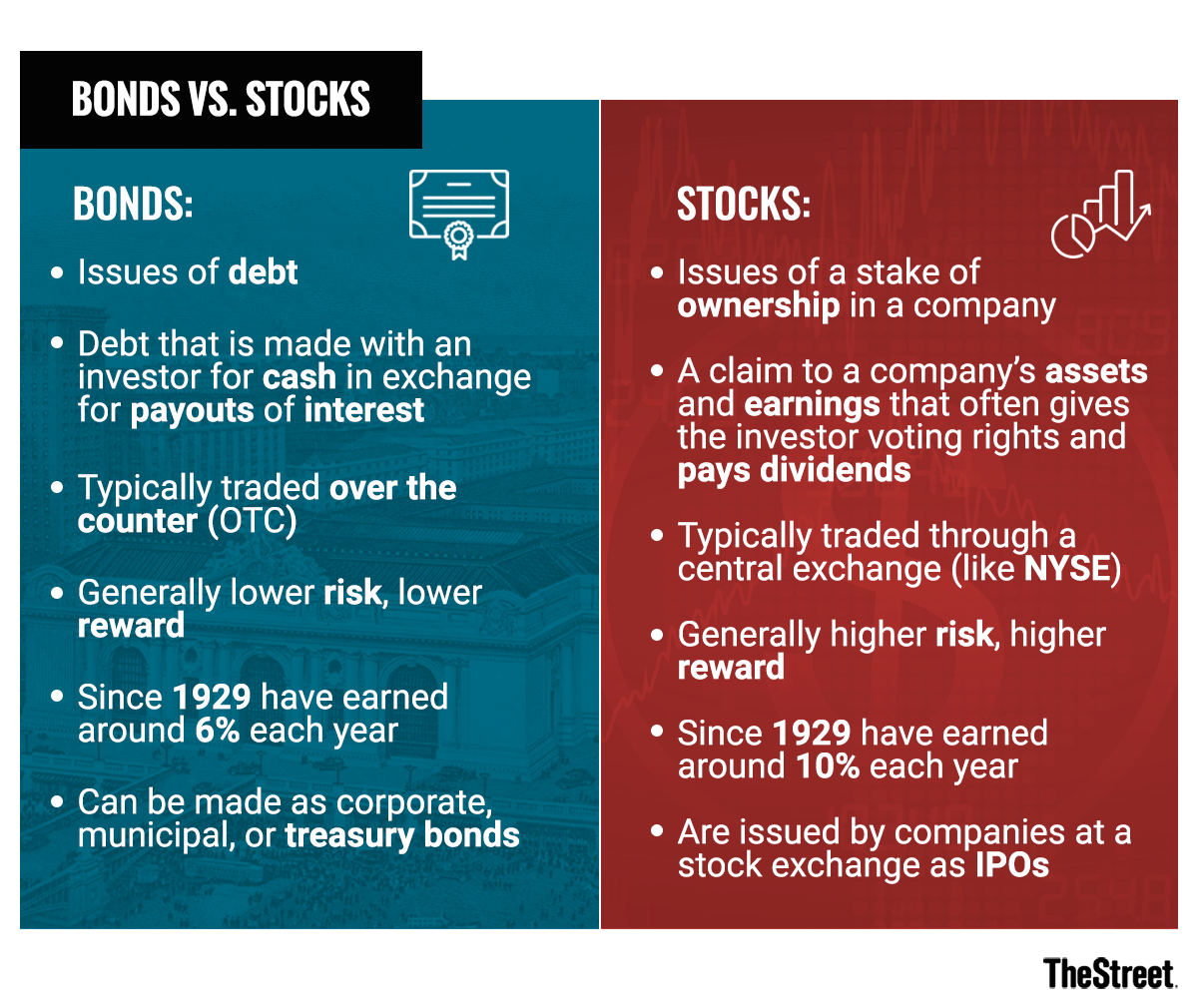
In the long run, stocks may provide you with a greater return on investment than securities like bonds can offer. Common stocks of major corporations are. What are some tips for investing in bonds? · Know when bonds mature. · Know the bond's rating. · Investigate the bond issuer's track record. · Understand your. Learn how to invest in stocks with this comprehensive beginner's guide. Discover the essential steps, tips, and strategies to start growing your wealth. Bonds are basically borrowing agreements. A bond is established as a contract between two parties where the one party lends money to the other in exchange for. Asset allocation: This refers to how you divide up your portfolio among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash alternatives, to help you work. Stocks are ownership shares in a company, while bonds are a kind of loan from investors to a company or government. To make a profit from stocks, you'll need to. Unit 6: Stocks and bonds · Introduction to stocks · What it means to buy a company's stock · Shorting stock · Shorting stock · Understanding company statements and. While stocks are ownership in a company, bonds are a loan to a company or government. Because they are a loan, with a set interest payment, a maturity date, and. This step-by-step guide for beginners can get you investing in the stock market, whether you want to use an online brokerage, robo-advisor or financial. In the long run, stocks may provide you with a greater return on investment than securities like bonds can offer. Common stocks of major corporations are. What are some tips for investing in bonds? · Know when bonds mature. · Know the bond's rating. · Investigate the bond issuer's track record. · Understand your. Learn how to invest in stocks with this comprehensive beginner's guide. Discover the essential steps, tips, and strategies to start growing your wealth. Bonds are basically borrowing agreements. A bond is established as a contract between two parties where the one party lends money to the other in exchange for. Asset allocation: This refers to how you divide up your portfolio among different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and cash alternatives, to help you work. Stocks are ownership shares in a company, while bonds are a kind of loan from investors to a company or government. To make a profit from stocks, you'll need to. Unit 6: Stocks and bonds · Introduction to stocks · What it means to buy a company's stock · Shorting stock · Shorting stock · Understanding company statements and. While stocks are ownership in a company, bonds are a loan to a company or government. Because they are a loan, with a set interest payment, a maturity date, and. This step-by-step guide for beginners can get you investing in the stock market, whether you want to use an online brokerage, robo-advisor or financial.
These are the most common tools of the trade and the basic building blocks of your portfolio. You'll also hear them referred to as asset classes. Before you. Shares are issued by firms, priced daily and listed on a stock exchange. Bonds, meanwhile, are effectively loans where the investor is the creditor. In return. The easiest way to understand bond prices is to add a zero to the price quoted in the market. For example, if a bond is quoted at 99 in the market, the price is. stocks and bonds and other elements of the market. There have been a number basic for carrying out certain investment processes. Depending on its. Stocks offer an opportunity for higher long-term returns compared with bonds but come with greater risk. Bonds are generally more stable than stocks but have. In general, bonds are usually seen as a less volatile investment than stocks. This is due to the stability of the bond market, and the fact that stock prices. “Equity” is a way to describe ownership, and “equities” are an alternative name for stocks. Companies can also issue bonds to raise capital, although buying. Stocks and Bonds for Beginners: Basics of investing in stock market. Bond investment. Trading crash course for beginners. Stock market day trading. When an investor buys a stock, part ownership in the form of a share is bought. · Bonds are a type of investment designed to aid governments and corporations to. A bond is a debt security, like an IOU. Borrowers issue bonds to raise money from investors willing to lend them money for a certain amount of time. When you. The greatest difference between stocks and bonds are their risk levels and their return potential. Speaking very generally, stocks have historically offered. You will learn about growth and dividend stocks and how to use market data. After completing this course, you will have an understanding of the two fundamental. When most people talk about investing, they're usually referring to investments in stocks, bonds and investment funds, which are all types of securities. If you. An introduction. What are stocks and bonds? 3. Determining the differences stock basics. 5. Understanding stocks bond basics. 9. Understanding bonds managing. Stocks differ from other investment classes, such as bonds, in several key ways. And no two individual stocks are exactly alike. That makes it important for. Why buy bonds? Bonds are issued by governments and corporations when they want to raise money. By buying a bond, you're giving the issuer a loan, and they. Companies can complete multiple secondary offerings of their stock when they need to raise additional funding, provided investors are willing to buy. Meanwhile. The most fundamental difference between stocks and bonds is the nature of the money used to purchase the instrument. In stocks, the money you invest buys you a. If you are young and saving for a long-term goal such as retirement, you may want to hold more stocks than bonds. Investors nearing or in retirement may want to. Stocks are equity instruments and can be considered as taking ownership of a company. While bonds are issued by all types of entities – including governments.